- What is Renewable energy?
- Geothermal Power Generation
- Wind Power Generation Mechanism
- Solar Power Generation Mechanism
- Current Status and Prospects of Renewable Energy
What is Renewable energy?
"Renewable energy" refers to energy sources that exist in nature and continue to be regenerated and supplied without depletion. Wind, water, sunlight, biomass, and geothermal energy are typical examples of renewable energy. These energy sources are attracting attention as sustainable energy with less impact on the environment. There is a growing demand for the expansion of renewable energy usage as a solution to the problems of global warming and the depletion of fossil fuels, and these facilities are being introduced globally. In recent years, local production for local consumption of renewable energy has been gaining attention. Local production for local consumption refers to the practice of consuming energy in the region where it is produced, aiming to reduce transportation costs, stimulate local economies, and achieve energy self-sufficiency. Wind power and solar power generation plans, in particular, are being rolled out according to the characteristics of each region, with the expectation that maximizing the use of local resources can also rejuvenate the local area.

Geothermal Power Generation
Geothermal power generation is a method of extracting energy from heat stored deep within the Earth to generate electricity. Deep beneath volcanoes, there is extremely hot magma, which produces thermal energy. In geothermal power generation, hot water or steam warmed by the heat from the magma is extracted from deep underground. This steam turns a turbine, which moves a generator, thus producing electric power.
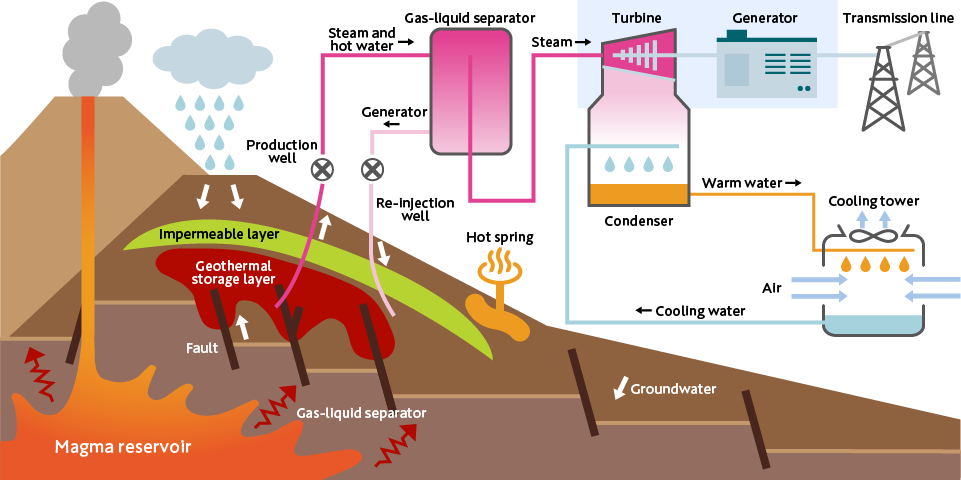
The Process of Geothermal Development
Geothermal development takes more than a decade. During this period, after obtaining the necessary permits and approvals, surface surveys are conducted to select promising sites for geothermal resources, drilling surveys are conducted to confirm the existence of geothermal resources, environmental assessments are carried out to reduce the impact on the environment and hot springs, and the construction of the power station is undertaken.
Just like oil and natural gas development, it involves extracting resources from deep underground to be used as energy, so you can't visually verify the extent of the resources. Therefore, time is spent on investigations and drilling to interpret the underground structure, with the aim of reducing uncertainty about the quantity of geothermal resources.
Surface Surveys
The goal is to select potential locations where hot water is likely accumulated deep underground and to calculate the amount of geothermal resources. This involves investigating areas like fumarole zones, hot springs, thermal alteration zones, and fault distributions. The methods include geological and geochemical surveys to study the surface conditions and geophysical explorations to investigate the underground conditions.

Drilling Surveys
Investigation wells are drilled with the purpose of confirming the existence and characteristics of the geothermal reservoir. The depth reaches between 1000 and 3000 meters, and the temperature reaches 200 to 300 degrees Celsius. If the reservoir is found, a fumarole test is conducted to extract fumaroles and hot water, and the amount of geothermal resources and power generation is assessed.
Types of Geothermal Power Generation
There are primarily three methods of geothermal power generation.
- Dry Steam Power Generation
- This method directly extracts steam from underground and uses it to turn a turbine. It's the simplest form of geothermal power generation and is used in areas where low amounts of hot water and high-temperature steam are emitted.
- Flash Steam Power Generation
- This is the most common way of power generation.
-
Single Flash Method: Geothermal fluid is drawn up from underground, divided into steam and hot water. The steam is used to power a turbine and generate electricity.
-
Double Flash Method: High-pressure steam and hot water-containing geothermal fluid is extracted from underground. In the single flash method, hot water that is not used for power generation can still be utilized; if the hot water is at high temperature and pressure, reducing the pressure can cause it to boil and become steam. The double flash method thus operates the turbine with both high-pressure steam directly obtained from the geothermal fluid and low-pressure steam obtained from hot water.
-
- Binary Cycle Power Generation
- This method uses underground hot water to evaporate a low-boiling-point liquid, and its steam powers a turbine. The characteristic feature of this method is its wide range of adaptability, as even relatively low-temperature geothermal resources can be utilized.
Advantages of Geothermal Power Generation
-
Sustainability: Because it uses geothermal energy from underground, there's no concern about depletion like in the case of fossil fuels, making it possible to supply electricity over a long period.
-
Stability: Since it uses steam from the wells regardless of the time of day, it's not affected by weather or season, enabling stable power generation 24/7, 365 days a year.
Challenges of Geothermal Power Generation
The main challenges of geothermal power generation are as follows:
-
Initial Investment: The risk of development is high as there are chances that steam may not be emitted even after drilling wells. Time and money are needed for geothermal resource investigation until the decision to commercialize the project is made. In Japan, some companies reduce their financial burden by using a system that provides partial subsidies for resource surveys to reduce development costs.
-
Geographical Constraints: Geothermal resources are concentrated in specific regions, and promising locations often overlap with areas where national parks and hot springs facilities are scattered. Therefore, sufficient discussions and adjustments with local governments and stakeholders are required.
-
Environmental Impact: Concerns about the impact on the local environment, such as geological changes and depletion of hot springs associated with the development of geothermal power stations, need to be thoroughly considered from the planning stage of the project to ensure that they will not pose problems.
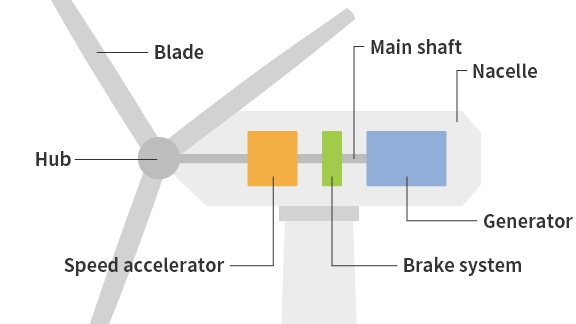
Wind Power Generation Mechanism
This is a method of generating electricity using the force of the wind. Windmill blades rotate when they catch the wind, and this rotational energy is transferred to a generator to produce electricity. Wind power generation facilities can be installed in both areas with good wind conditions on land and at sea. In Japan, while the installation of onshore wind power is advancing, the introduction of offshore wind power, which holds significant potential due to less land constraints in the island nation, is highly expected.
Potential Sites for Wind Power Generation
Naturally, potential locations are selected based on good wind conditions and considerations such as connection points to deliver the electricity generated to the grid. Moreover, when installing offshore wind facilities, permission for sea area occupancy is necessary. In Japan, areas designated as promotion regions go through a public bidding process for business operations, and the operators selected through this process typically receive permission to occupy the sea area. Selection criteria evaluate harmony with the region and economic impacts; hence, project plans are formulated after thorough discussions with regional stakeholders.
Advantages of Wind Power Generation
The main advantages of wind power generation are as follows:
-
Economy: It is considered an economically viable power generation method as the cost of generating electricity can be comparable to thermal power generation when facilities are installed on a large scale.
-
Conversion Efficiency: Depending on the height of the windmill and the blades, it is said to be a technology that can convert wind energy into electrical energy at a high efficiency.
-
Activating Local Economy: The construction and operation of wind power plants contribute to creating employment opportunities and advancing the economic development of a region. Especially, offshore wind power projects often tend to be large-scale, and contributions to the area through the development and operation of power stations generate high expectations in the region.
Challenges of Wind Power Generation
The main challenges of wind power generation are as follows:
-
Weather Dependence: The power output from wind energy can be unstable and fluctuate depending on the strength and direction of the wind.
-
Landscape and Noise: Wind turbines at wind power stations could potentially harm the scenery due to their visual size, and the noise produced by the rotation of the wind turbines could be problematic for nearby residents. These issues need consideration from the planning stage itself.
Solar Power Generation Mechanism
This is a technology that converts sunlight into electricity. Solar cells, composed of semiconductors made from silicon, are typically used to convert light energy directly into electrical energy, which is then utilized as power. The electricity generated by solar cells is direct current (DC), so the power generated at large-scale solar power stations is converted to alternating current (AC) using a device called a power conditioner and is then transmitted to the power grid.
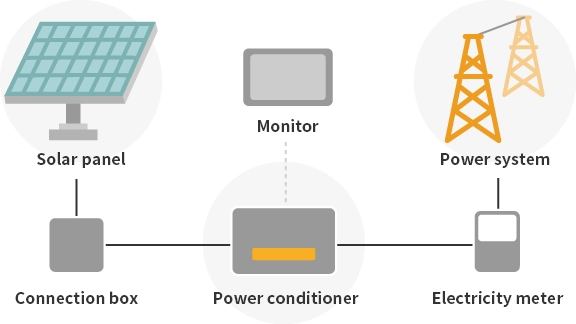
Potential Sites for Solar Power Generation
To obtain more electricity, it is necessary to install large-scale facilities in regions with high solar radiation. However, facilities can also be introduced on a scale suitable for locations with limited available land. The power generated by solar cells is transmitted through power lines owned and managed by local power transmission and distribution operators, so generally, locations where connection points to these power lines can be installed near the power station are candidate sites. Furthermore, if the land has been leveled, the installation work for solar cells can be reduced, making sites like former factories suitable candidate locations.
Advantages of Solar Power Generation
The main advantages of solar power generation are as follows:
-
Easy to install: The energy source is sunlight, so the solar intensity will differ according to the region. Fundamentally, there are no constraints on where it can be installed, and it is not restricted to large-scale operations. It can be installed on the roofs of single-family homes or buildings which makes it a highly practical generation method for small-scale systems.
-
Running cost: It is said that the operating cost is lower than other power generation methods because it does not require extensive maintenance after installation.
-
Emergency power source during disasters: It can be used as an emergency power source during power outages in disasters because of the ability to install small-scale generation systems anywhere without geographical or location constraints.
-
Difference from solar thermal power generation: Solar thermal power generation is another setup that utilizes the energy of the sun. It was expected to be adopted due to its higher energy efficiency compared to solar power generation. However, in recent years, the wide proliferation of solar power worldwide, not limited to Japan, has been made possible due to the affordability of solar cells on a global scale and because solar power generation can be installed on a smaller scale compared to solar thermal power.
Challenges of Solar Power Generation
The main challenges of solar power generation are as follows:
Current Status and Prospects of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy generation has various challenges such as weather dependency, lack of large-scale land/land usage, and high costs. However, in order to reduce CO2 and achieve a sustainable society, these challenges must be overcome. For instance, systems that can stably supply power generated by renewable energy, through storage batteries, even on calm nights and in non-windy conditions are starting to gain popularity in solar and wind power generation. Also, perovskite solar cells, which are thin, lightweight, flexible, and can be installed in places that were difficult to set up with previous technology, are drawing attention as next-generation solar cells. It is expected that the introduction of renewable energy will progress through new initiatives and business models that solve the conventional challenges of renewable energy.
To contribute to the resolution of renewable energy challenges and the expansion of its adoption, INPEX is engaged in renewable energy operations such as geothermal and offshore wind power in Japan and overseas, leveraging the knowledge and experience cultivated in the Oil and gas development fields.