What are CCS and CCUS?
The world's dependence on fossil fuels remains high, and the energy transition needs to simultaneously address energy demand and decarbonization. Measures to reduce CO2 emissions, a greenhouse gas, are indispensable to achieve global warming countermeasures and carbon neutrality. In such a context, a technology called carbon capture and storage (CCS) has become a trump card for achieving carbon neutrality.
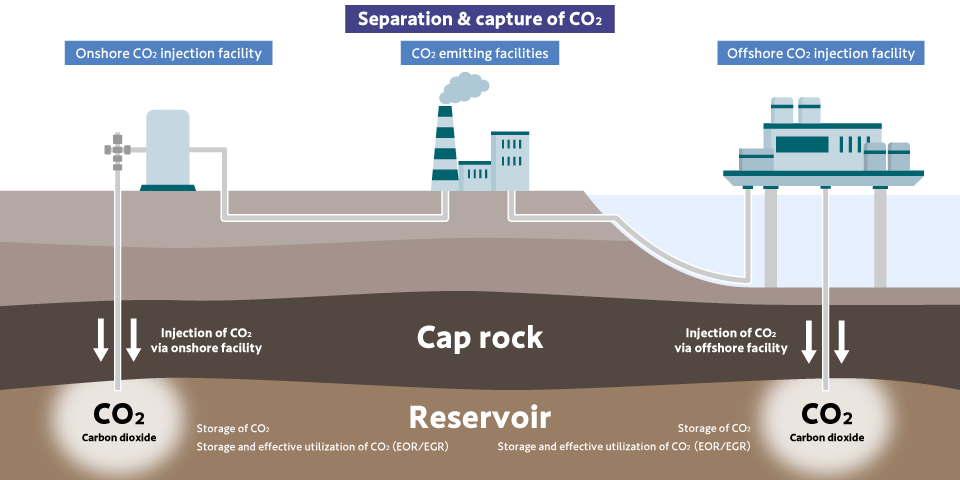
CCS refers to the technology of separating and recovering CO2 emitted from power plants and chemical plants from other gases, then storing it deep underground. When the CO2 separated and stored by CCS is reused to create fuels, plastics and the like, or utilized in oil recovery, this technology is referred to as CCUS, an abbreviation for Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage.
Why is CCS/CCUS attracting attention now?
Based on the 'Paris Agreement', an international framework for climate change issues, CCS/CCUS technology is attracting attention to achieve greenhouse gas reduction targets. There are challenges in reducing CO2 emissions in hard-to-abate industries such as steel, cement and chemical production, oil refining and power generation, where it is challenging to meet CO2 emission reduction targets with energy-saving, electrification, and hydrogenation measures alone. However, even in such fields, CCS/CCUS can be used to control CO2 emissions, making it an indispensable technology for achieving carbon neutrality.
Safety of CCS
Repeated demonstration tests have been carried out, confirming the consistent operation and safety from separation and recovery to injection and storage. Also, through various monitoring and marine environmental surveys, it has been confirmed that CCS is a safe and reassuring system.
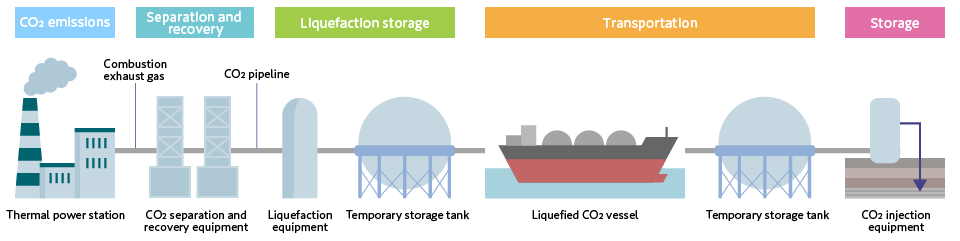
CCS/CCUS Business Value Chain
Suitable locations for CCS/CCUS
The conditions for suitable locations include ① having CO2 storage potential and ② being near regions with high CO2 emissions. Based on surveys conducted so far, regions such as Australia, Malaysia, and Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, are believed to have high storage potential. Furthermore, as the demand for LNG in Southeast Asian countries is expected to grow in the future, CCS projects are also anticipated as a means to reduce CO2 emissions in LNG projects in these regions.
CCS Business Value Chain (Case when transported to the storage site by ship)
emission, separation/collection, storage, transportation and sequestration. It is required that various business operators participate and collaborate to build a value chain.
Our Strengths
CCS/CCUS is a field that can leverage the subsurface technologies such as reservoir evaluation technology and drilling technology that INPEX has enhanced over the years in upstream development of oil and natural gas. Also, LNG projects are sectors where the implementation of CCS is progressing, and there is a benefit of being able to advance decarbonization projects while meeting the growing demand for LNG, which is expected as a transitional energy.
Our company has defined CCS as one of the focus areas towards net-zero carbon, and we will introduce it at both the Ichthys and Abadi LNG projects. For the time being, in addition to reducing CO2 emissions from our own operations through CCS, we are also planning to launch businesses that cater to the CO2 reduction needs of other companies.
Current Status and Prospects of CCS/CCUS
Challenges and Initiatives for Realizing CCS in Japan
Technical Issues
To commercialize CCS, it is necessary to establish technology, reduce costs (including the construction costs of CCS facilities and operating costs), and develop suitable storage sites in each process of separation/collection, transportation, and storage. Therefore, we, as business operators, are working in cooperation with the Japanese government and business operators who are responsible for each area of the value chain, to work towards reducing costs across the entire CCS value chain, including separation/collection, transportation, and storage.
Challenges in Legal Preparations
Environmental preparations for the development of suitable locations and the commercialization of the CCS are also important. It is crucial to establish new "CO2 injection and storage rights", clarify the legal responsibilities that the business operators should bear, and properly manage the storage layers. Ensuring that business operators can appropriately evaluate and manage risks is a prerequisite for investment decisions by companies and financial institutions.
In Japan, the "Law on Carbon Dioxide Storage Business" (CCS Business Law) was established in May of Reiwa 6 (2024). Under this law, the government designates areas where CO2 can be stored and issues permits for CCS businesses to operators selected through a public offering. Operators granted permission are given "exploratory drilling rights" to drill and confirm whether the geological formation is suitable for CO2 storage, and "storage rights" to actually store CO2. Operators are also obligated to monitor whether CO2 is leaking and secure the necessary funds for the future.
Ensuring Social Acceptability
It is crucial to progress the CCS with the understanding of those in the storage areas. Business operators are required to provide detailed explanations to local governments and stakeholders, and it's significant for the national government to make efforts to gain understanding about the policy significance of CCS and the latest findings. In the Ichthys LNG project in Australia, where our company operates, we have been advancing the development while obtaining the understanding of the local residents through careful disclosure and explanation. Similarly, in CCS projects, we will carefully explain the safety and environmental impact of CCS, striving to ensure social acceptance.
Advanced CCS Projects
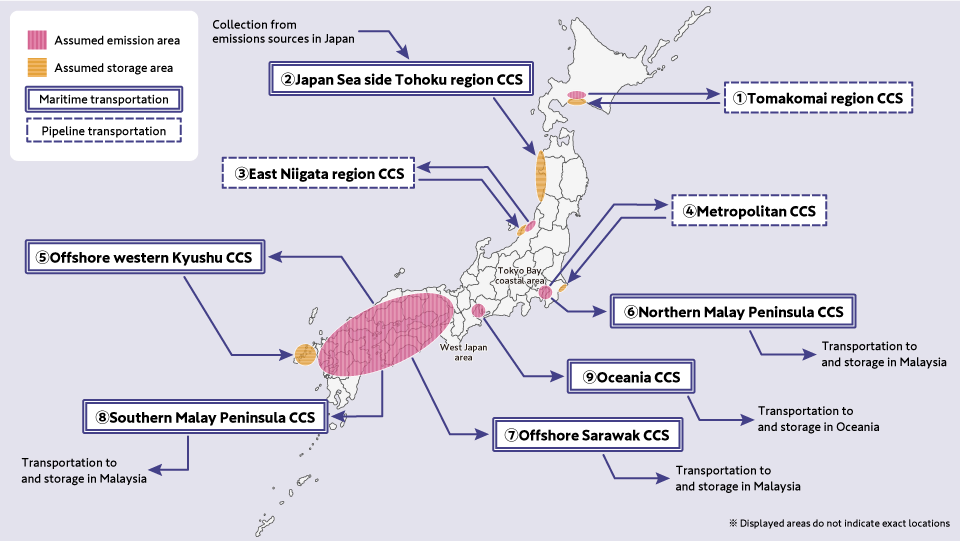
JOGMEC has publicly solicited commissioned projects for a survey aimed at commercializing domestic CCS projects by fiscal 2030. Among those, INPEX is involved in "Metropolitan Area CCS" and "Tohoku Region on the Sea of Japan Side CCS," with our company leading the consortium for the "Metropolitan Area CCS". In fiscal 2024, a new public offering was made for "Design work, etc. for advanced CCS projects," and both projects were selected (out of 9 projects in total).
Each of the selected projects are extremely important as they comprise CCS projects targeting domestic CO2 emitters. They are important not only for creating our new business foundation but also for contributing significantly to the reduction of CO2 within Japan. We will accumulate the drilling technologies and pipeline transportation technologies we have cultivated so far and strive for the realization of these projects.
https://www.jogmec.go.jp/english/news/release/news_10_00072.html
Our company is considering and participating in many CCS/CCUS projects both domestically and internationally. By introducing CCS to LNG, which has excellent environmental characteristics, to make it even cleaner, and by developing clean energy such as renewable energy, hydrogen, and ammonia, which we are focusing on, we will continue to lead the industry as a major player in the energy sector into the future.
The Progress of Our CCS/CCUS Projects